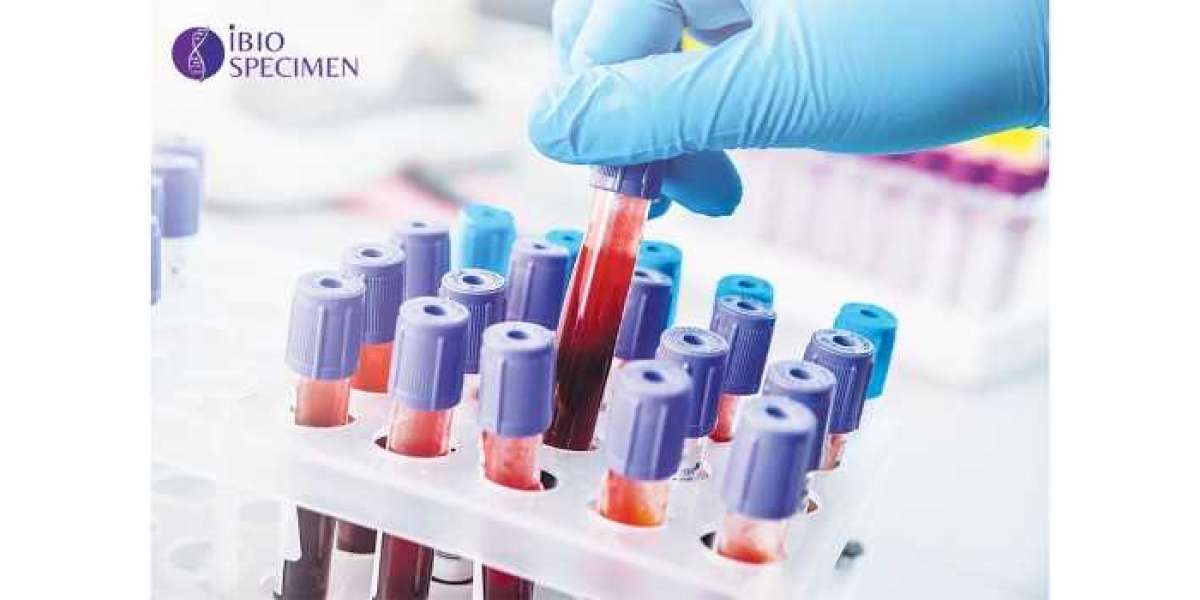
In the dynamic world of medical and scientific research, selecting the appropriate human biofluids for your study is a critical decision that can greatly impact the outcomes and validity of your research. Human biofluids, such as blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and saliva, are rich sources of information that can provide valuable insights into various diseases, biomarkers, and physiological processes. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to choose the right human biofluids for your research, ensuring that your investigations yield meaningful results.
Understanding the Types of Human Biofluids
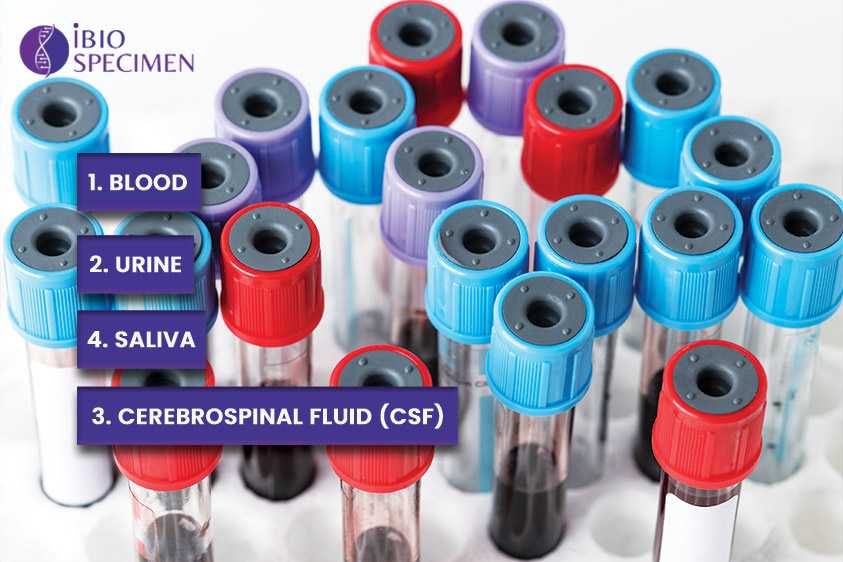
Before diving into the selection process, it's important to have a solid understanding of the different types of human biofluids available for research. Here are some common biofluids and their key characteristics:
- Blood
Characteristics: Blood is a complex biofluid that contains various components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. It is rich in proteins, hormones, metabolites, and genetic material (DNA and RNA).
Applications: Blood is commonly used in clinical and research settings to study diseases, monitor biomarkers, and assess overall health. It can provide insights into conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
- Urine
Characteristics: Urine is a waste product excreted by the kidneys. It contains metabolites, electrolytes, hormones, and waste products. Urine samples are non-invasive and easy to collect.
Applications: Urine analysis is often used to diagnose kidney diseases, monitor drug use, and study metabolic disorders. It can also be used for early detection of certain diseases.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Characteristics: CSF is a clear, colorless fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It contains proteins, glucose, and cells. Obtaining CSF requires a lumbar puncture procedure.
Applications: CSF analysis is vital in diagnosing neurological conditions such as meningitis, multiple sclerosis, and intracranial hemorrhage. It can also be used for research on brain-related diseases.
- Saliva
Characteristics: Saliva is a watery fluid produced by salivary glands. It contains enzymes, electrolytes, hormones, and antibodies. Saliva samples are non-invasive and easy to collect.
Applications: Saliva is increasingly used in research for studying oral diseases, hormonal fluctuations, and even as a potential diagnostic tool for systemic conditions like diabetes.
Steps to Choose the Right Human Biofluids
Now that you have a grasp of the types of human biofluids available, let's explore the steps to select the most suitable biofluid for your research:
- Define Your Research Objectives
Start by clearly defining your research goals and objectives. What specific questions are you trying to answer? Understanding your research focus will guide your biofluid selection.
- Consider the Biomarkers of Interest
Identify the biomarkers or analytes you plan to study. Different biofluids may contain varying levels of specific biomarkers. Ensure that the biofluid you choose aligns with your biomarker of interest.
- Evaluate Sample Availability
Assess the availability of the chosen biofluid. Some biofluids, like blood and urine, are readily accessible, while others, such as CSF, may require more invasive procedures. Availability can impact the feasibility of your study.
- Analyze Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Consider ethical and regulatory factors when working with human biofluids. Ensure that you have the necessary approvals and informed consent from participants if required by your research institution and ethics board.
- Weigh Cost and Resources
Evaluate the financial and logistical aspects of obtaining and processing the chosen biofluid. Some biofluids may be more cost-effective or easier to handle than others.
- Assess Sample Stability
Different biofluids have varying stability profiles. Consider the time and conditions required to collect, store, and transport samples to ensure their integrity for analysis.
- Seek Collaboration and Expert Advice
If you are unsure about your biofluid selection, seek advice from experts in your field. Collaborating with experienced researchers can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right human biofluids for research is a crucial step that can significantly impact the success and relevance of your study. By understanding the characteristics and applications of different biofluids, defining your research objectives, and considering ethical, logistical, and analytical factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your research goals. Ultimately, selecting the appropriate biofluids will enable you to unlock valuable insights and contribute to the advancement of medical and scientific knowledge.