Introduction
In the realm of modern manufacturing, CNC machine tools have revolutionized the way products are created. These machines combine precision engineering with computer technology to automate and enhance various industrial processes. This article delves into the world of CNC machine tools, exploring their history, functions, applications, and the transformative impact they have had on manufacturing industries.
Understanding CNC Machine Tools
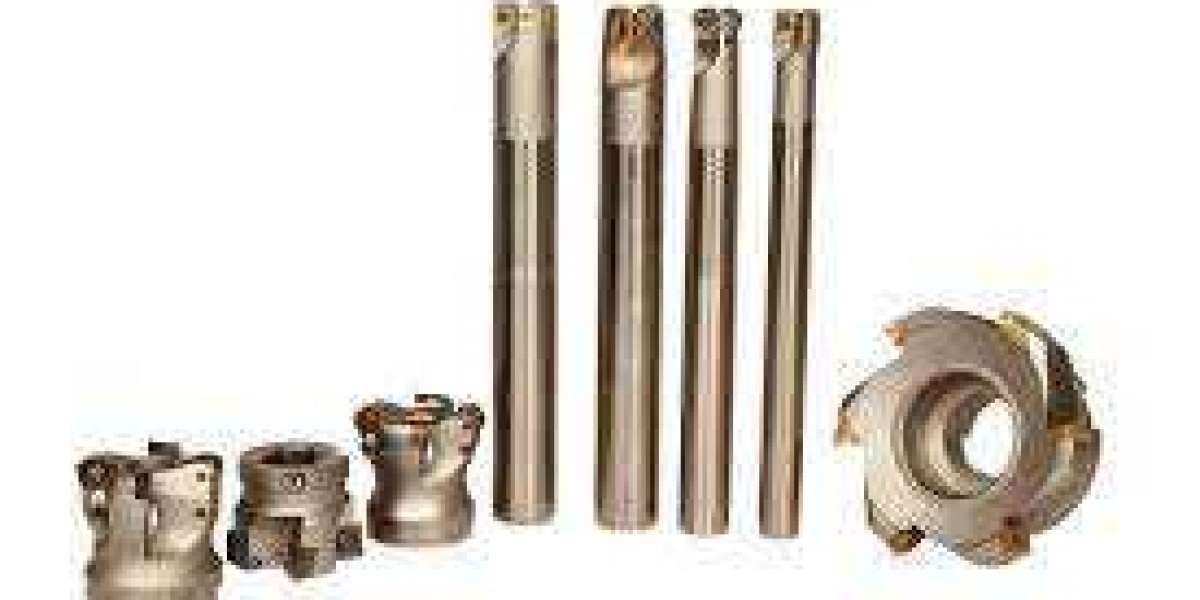
CNC machine tools are a class of automated equipment used in various manufacturing sectors to produce intricate components with high precision and repeatability. Unlike conventional manual machines, CNC machines are controlled by computer programs that dictate the movement and operation of cutting tools, resulting in faster production cycles and superior quality outputs.
Historical Evolution
The roots of CNC technology can be traced back to the mid-20th century. Early numerical control (NC) systems were developed to control machine tools using punched tape. However, it was the integration of computers that marked a significant turning point. In the 1970s and 1980s, CNC machines began to utilize microprocessors and digital interfaces, making them more versatile and user-friendly.
Key Components and Functionality
A typical CNC machine consists of several core components:
Controller: The brain of the CNC machine, the controller interprets computer-generated code and coordinates the machine's movements and operations.
Machine Tool: This includes various types such as lathes, milling machines, routers, and grinders. Each machine tool performs specific tasks like cutting, drilling, or shaping.
Tooling: Cutting tools, drills, and other accessories are crucial for shaping the raw material according to the programmed specifications.
Workpiece Holder: To ensure precision, the workpiece is securely held in place while the machine tool performs its operations.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) Software: CAD software is used for designing the product, while CAM software generates the code that guides the CNC machine's actions.
Advantages of CNC Machine Tools
Precision: CNC machines can execute tasks with unmatched accuracy, resulting in consistent, high-quality products.
Automation: Once programmed, CNC machines can work autonomously, freeing up human operators for more complex tasks.
Efficiency: CNC machines are capable of running 24/7, reducing production lead times and increasing overall efficiency.
Flexibility: Reprogramming CNC machines allows for rapid changes in production, enabling manufacturers to adapt to new designs and demands quickly.
Applications
CNC machine tools find applications across a wide range of industries:
Automotive: CNC machines are used to manufacture engine components, chassis parts, and intricate molds.
Aerospace: They produce complex parts like turbine blades and structural components with high precision.
Medical: CNC machines create surgical instruments, prosthetics, and intricate medical devices.
Electronics: They manufacture printed circuit boards, connectors, and microelectronics components.
Future Trends
As technology continues to advance, CNC machine tools are also evolving. Some future trends include:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI algorithms can optimize machining processes, predict tool wear, and enhance overall efficiency.
Additive Manufacturing Integration: CNC machines may be combined with 3D printing technologies for hybrid manufacturing processes.
IoT Connectivity: CNC machines equipped with sensors can enable remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analysis.
Conclusion
CNC machine tools have undoubtedly transformed the manufacturing landscape, enabling higher precision, efficiency, and flexibility. From their humble beginnings to their integration with cutting-edge technologies, these machines continue to play a pivotal role in shaping industries worldwide, paving the way for innovative and efficient production processes.